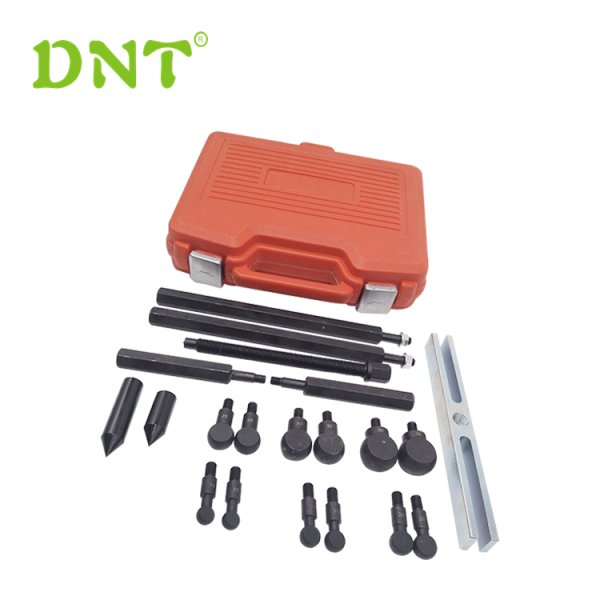
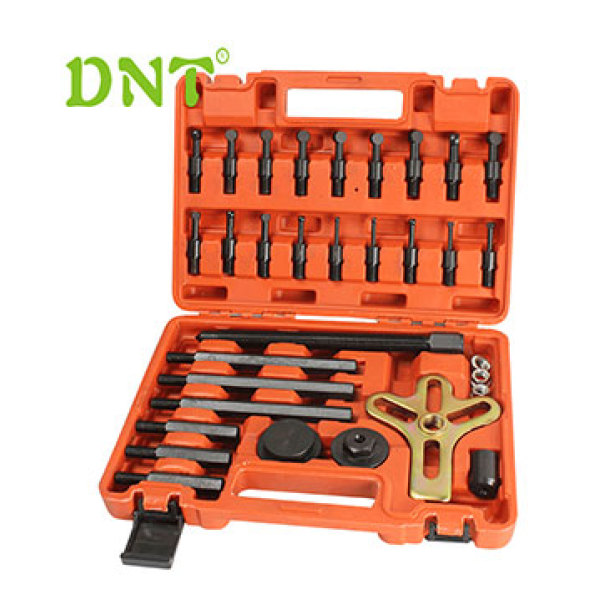
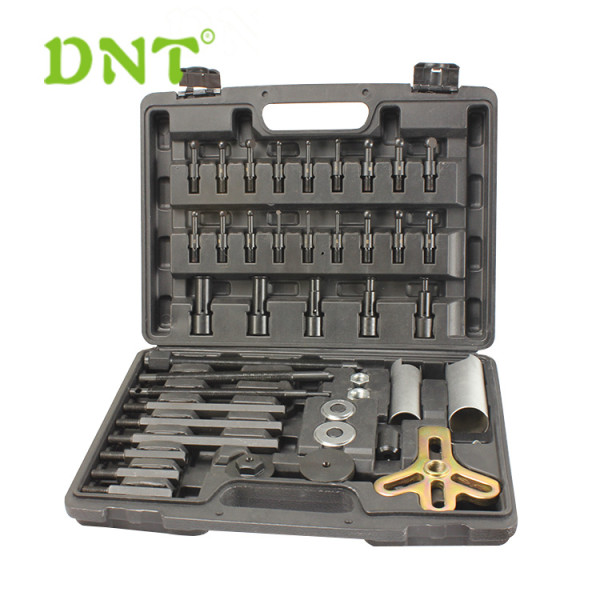
Solution for Deep Groove Ball Bearing Removal and Tools recomment
What is ball bearing?
A ball bearing is a type of rolling-element bearing that uses balls to maintain the separation between the bearing races.
The purpose of a ball bearing is to reduce rotational friction and support radial and axial loads. It achieves this by using at least two
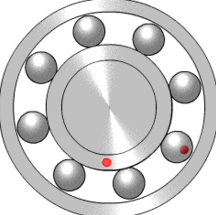
races to contain the balls and transmit the loads through the balls. In most applications, one race is stationary and the other is attached to the rotating assembly (e.g., a hub or shaft). As one of the bearing races rotates it causes the balls to rotate as well. Because the balls are rolling they have a much lower coefficient of friction than if two flat surfaces were sliding against each other.
Ball bearings tend to have lower load capacity for their size than other kinds of rolling-element bearings due to the smaller contact area between the balls and races. However, they can tolerate some misalignment of the inner and outer races.
How to replace when ball bearing is broken
Step
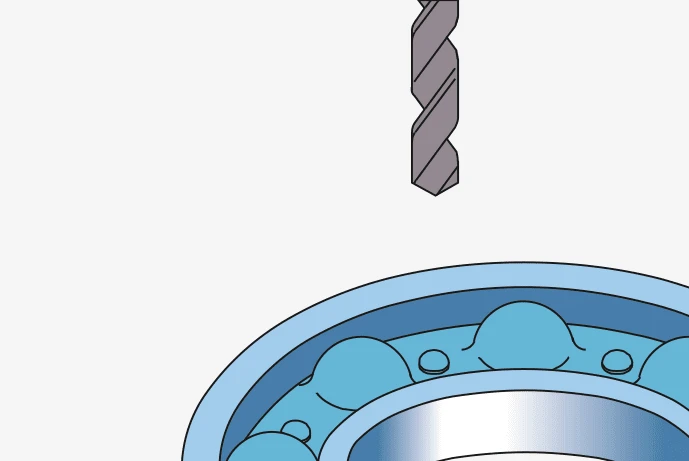
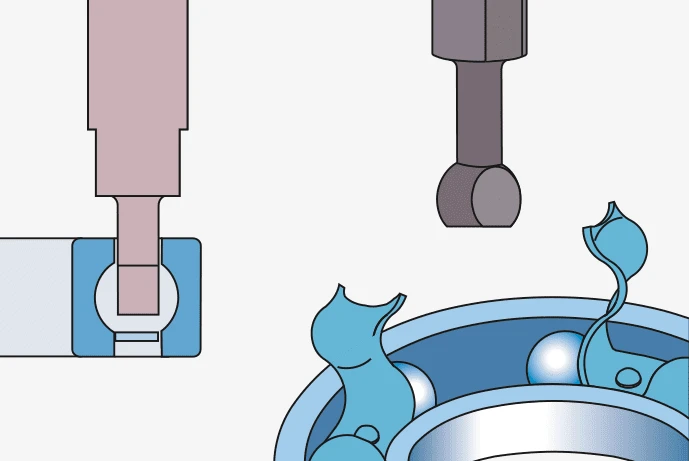

Remove seal and open selected Insert appropriate bearing adapter Insert the second adapter into
section of ball cage. and rotate it 90° ensuring positive prepared area diametrically
grip within the bearing race. opposed.
The professional tools is recommend following
Leading Chinese tool company supplier wholesale high quality ball bearing puller tool to extractor bearings,Made in China
The Blind housing puller kit is an adapter-type puller for dismounting deep groove ball bearings in blind housings.
The deep groove ball-bearing puller is an adapter-type puller for dismounting deep groove ball bearings in blind housings.



